Erik Draeger (15-LW-029)
Abstract
Computational fluid dynamics plays an increasingly important role in numerous fields, including microfluidics, hydraulic fracturing, biosecurity, and circulatory disease modeling. Advances in high-performance computing and multiphysics algorithms have made it possible to model fluid flow through a variety of complex geometries with unprecedented fidelity. We propose combining LLNL's expertise in additive manufacturing and high-performance computing to create a new tightly coupled validation technique. By carrying out experiments on three-dimensional printed geometries generated from the same input meshes used in fluid dynamics simulations, we will be able to directly compare experiment and theory. We will apply this technique of additive manufacturing to validate current research into high-resolution simulation of the human circulatory system with explicit red blood cells that is being conducted on Livermore's Blue Gene/Q supercomputer. With this project we will, for the first time, investigate the cell- and patient-specific parameters that are most effective in metastatic cancer site prediction by creating a novel technique for profiling adhesion likelihood in the circulatory system for secondary tumor site formation based on a representative range of patient characteristics and cancer cell types. The rapid feedback loop enabled by this research will be used to direct large-scale simulations of cancer metastasis with explicit red blood cells and circulating tumor cells.
We expect to directly validate fluid dynamics simulations in complex geometries to quantify and improve the accuracy of multiphysics simulations for biological applications. Such a study requires a combination of both high-performance computing and additive manufacturing expertise. Additive manufacturing, or three-dimensional printing, enables fabrication of highly complex, three-dimensional structures with embedded hollow channels. This is a sound approach for creating replicas of complex biological structures that would be very difficult or impossible to create in any other way. We are able to use three-dimensional reconstructions of actual human vasculature, modify the design to add connections for fluidic flow control and diagnostic instruments, and then print it to create a basically identical match to the design file. We will use this technique to inform the accuracy of multiphysics terms needed to model circulatory disease, which will be used in large-scale simulations of cancer metastasis. These results will be of broad interest to the fluid dynamics and biology communities, and clinical collaborators will help develop risk assessment tools.
Mission Relevance
With simulation playing an increasingly important role in NNSA and LLNL missions, the use of additive manufacturing to directly quantify individual terms in a multiphysics calculation would be a powerful tool for verification and validation. This research has specific applications to microfluidics and bioscience and bioengineering, but the lessons learned from closely coupling theory and experiment will be useful for directly validating other applications as well, supporting the Laboratory core competencies in high-performance computing, simulation, and data science and advanced materials and manufacturing.
FY15 Accomplishments and Results
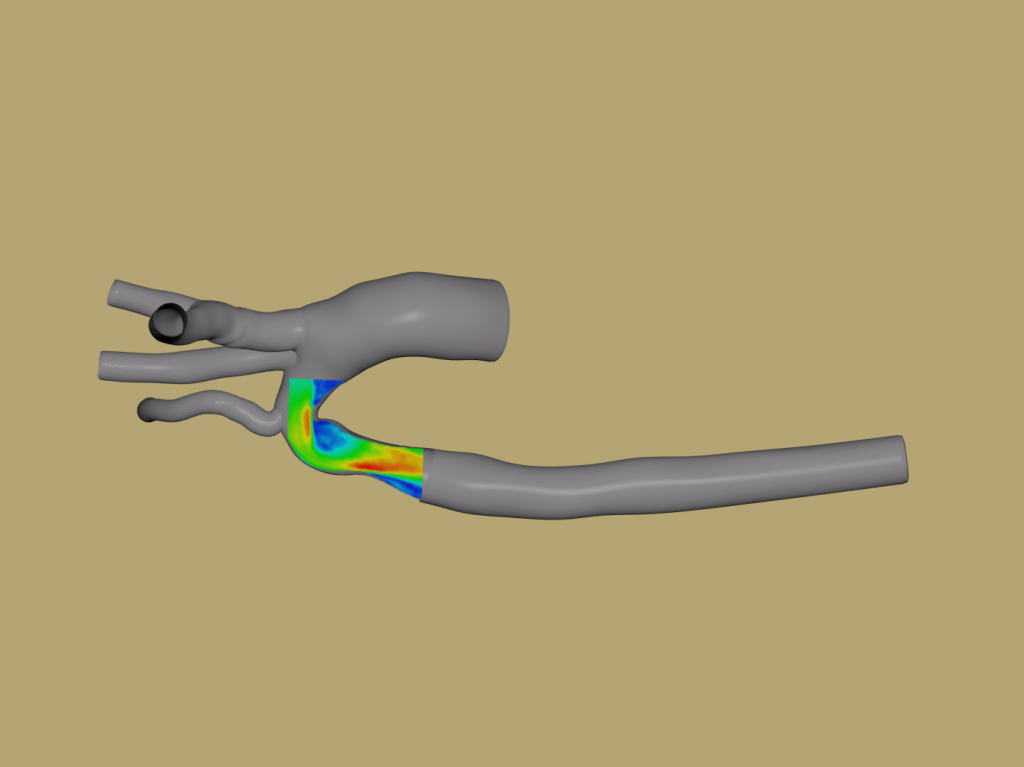
In FY15 we (1) scaled our simulation to use the full Livermore Sequoia supercomputer capabilities at 96% parallel efficiency, (2) created three three-dimensional geometries and performed correlated particle-image-velocimetry fluid experiments (a laser optical measurement technique for flow and turbulence) for model validation, and (3) investigated cell tracking methods in our model.
Experimental fluid velocity measurements of three-dimensional printed arterial geometry, overlaid on simulation geometry.
Publications and Presentations
- Randles, A., et al., Massively parallel models of the human circulatory system. SC 2015, Austin, TX, Nov. 15–20, 2015. LLNL-CONF-670030.
- Randles, A., E. W. Draeger, and P. E. Bailey, "Massively parallel simulations of hemodynamics in the primary large arteries of the human vasculature." J. Comput. Sci.-Neth. 9, 70 (2015). LLNL-CONF-666133. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2015.04.003